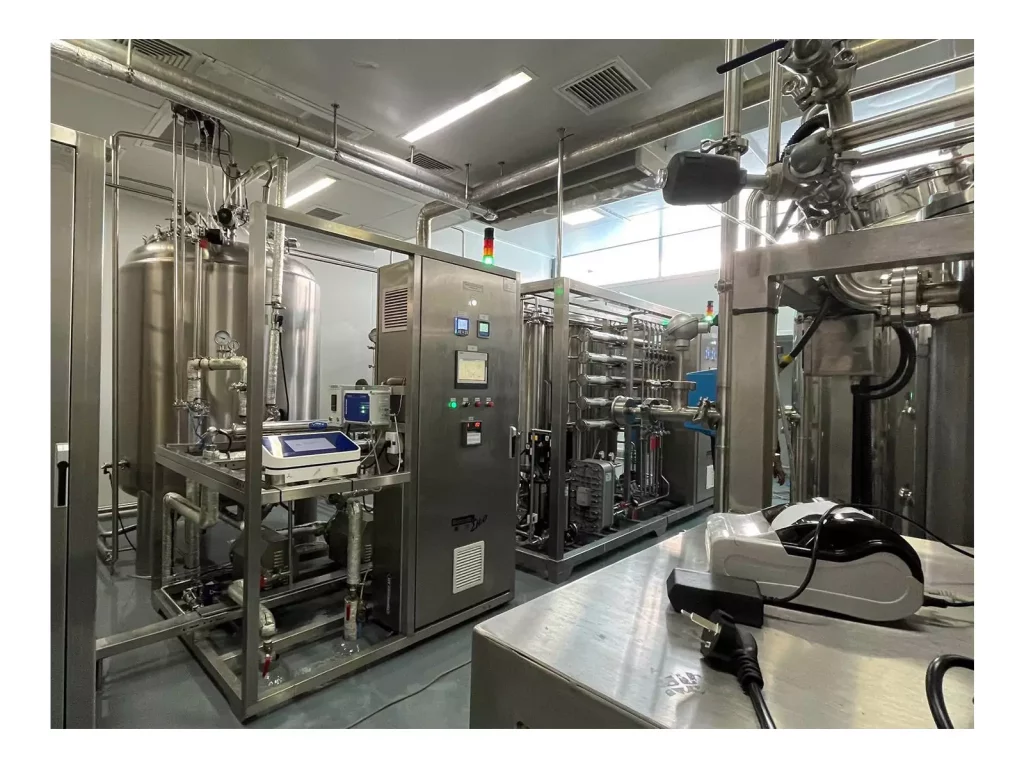
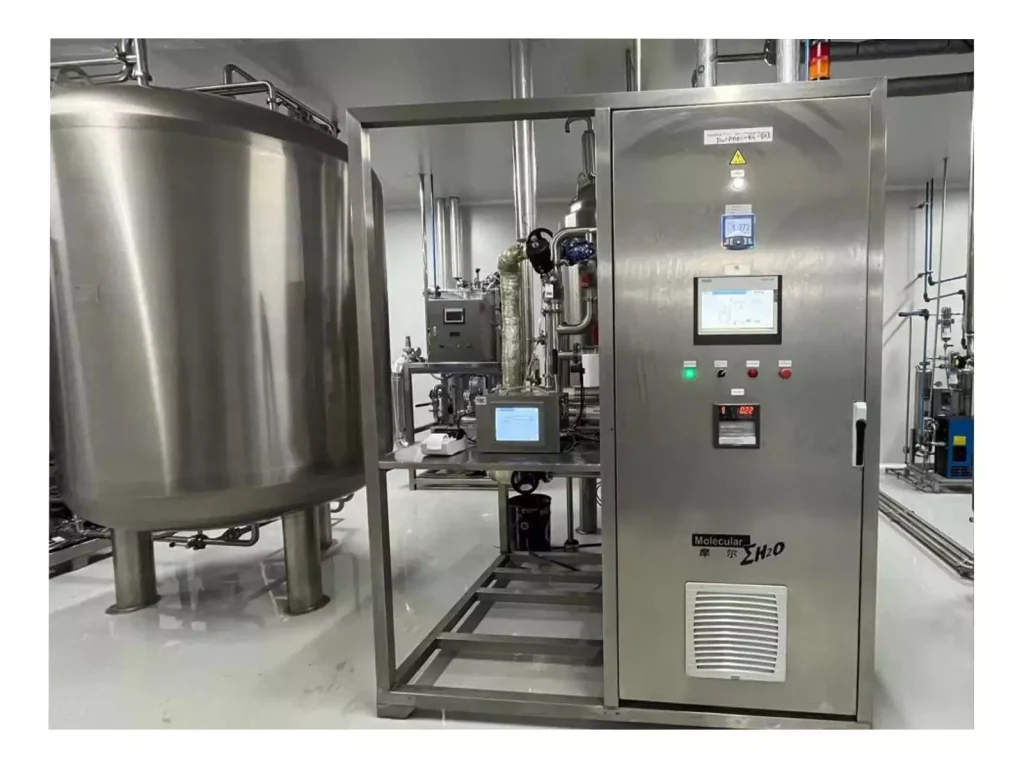
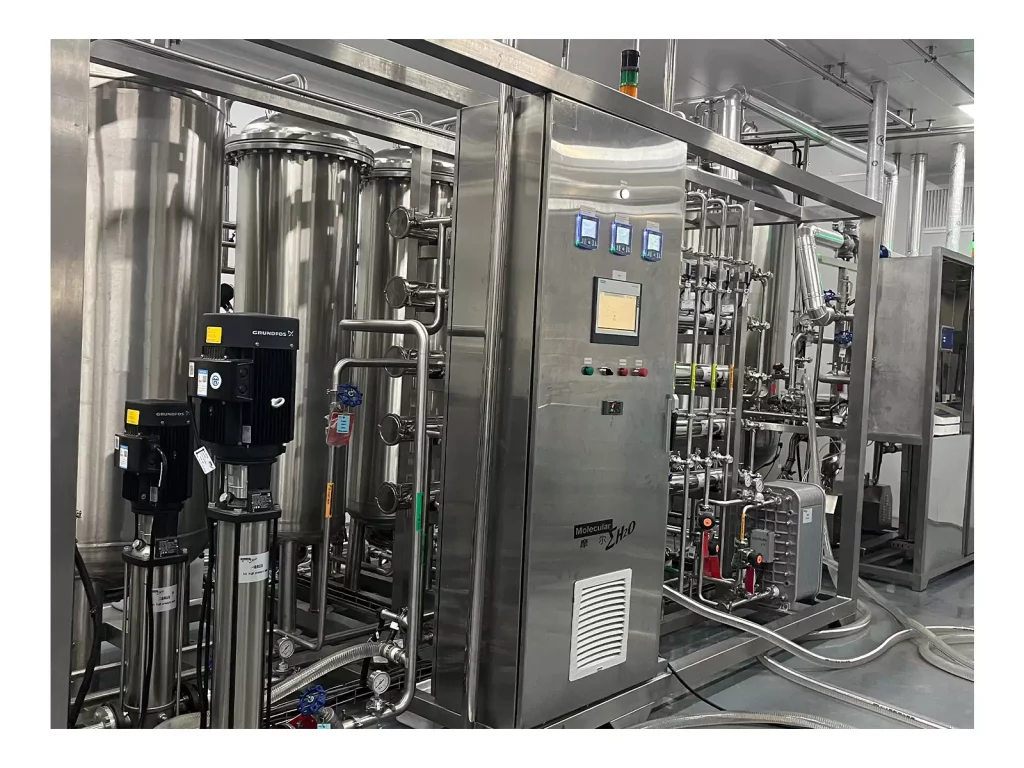
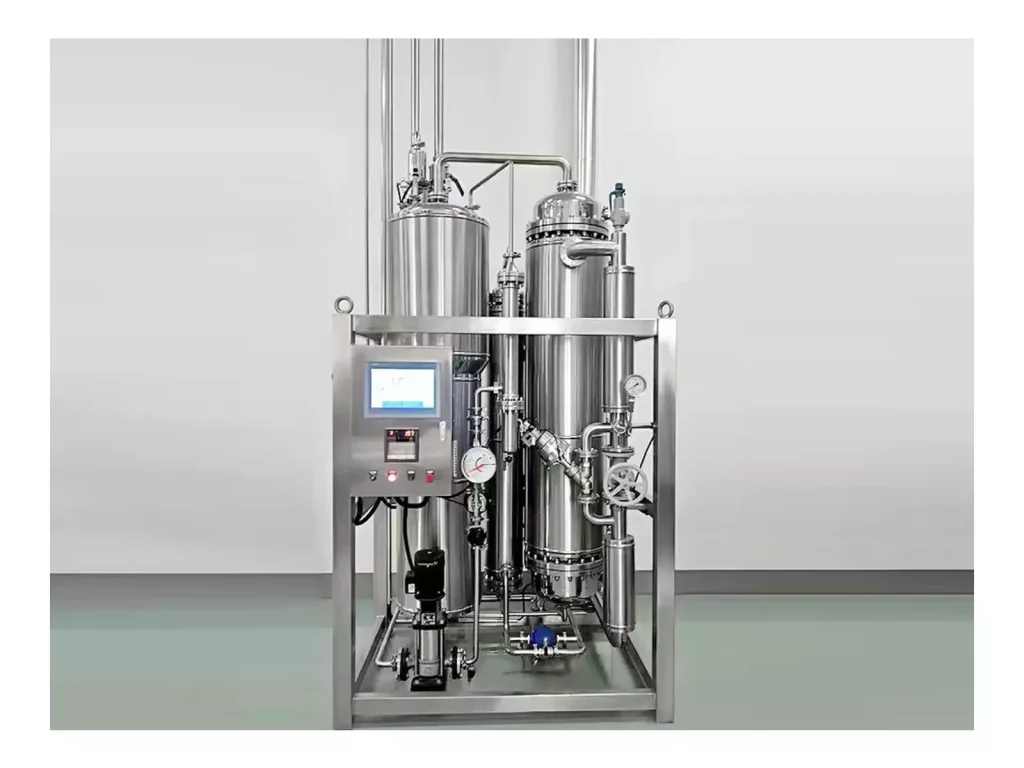
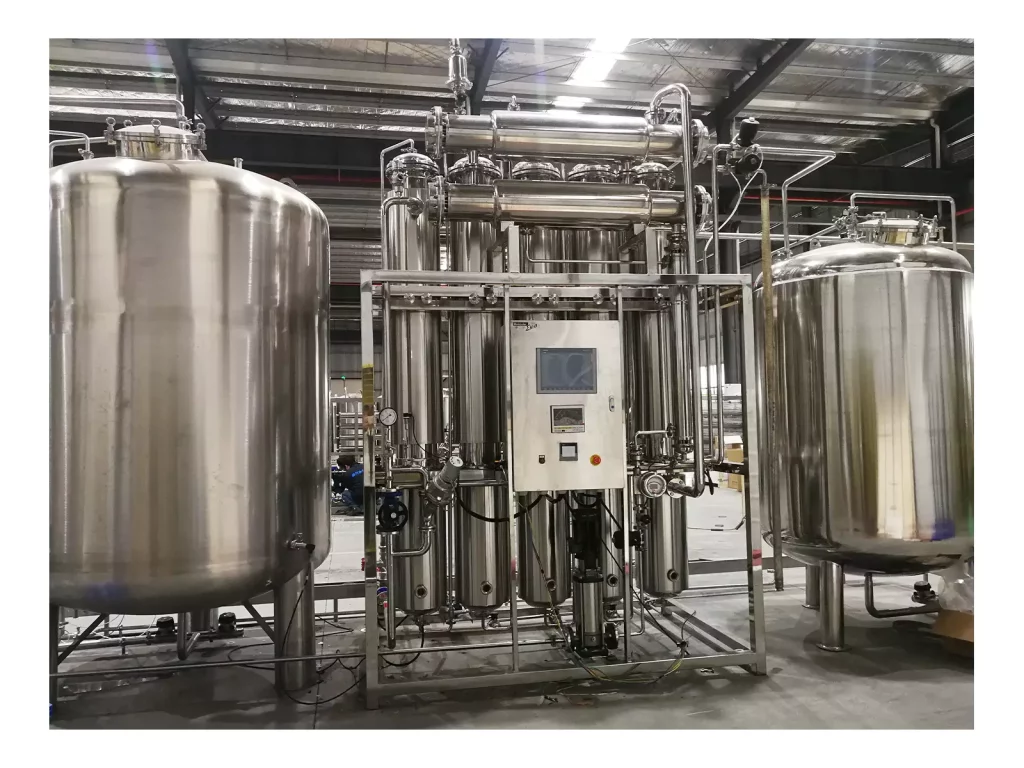
Pure water (PW) is a cornerstone of the water treatment process within the world of pharmacy. It is employed in nearly every aspect of manufacturing pharmaceuticals, from formulation of the drug and equipment rinsing to cleaning and diluting of the ingredients. Making sure that the purity and consistency of water that is purified water for pharmaceutical use is essential, not only when it comes to creation, but throughout the Purified Water Storage and Distribution System. Poorly designed PW systems could increase endotoxin levels, microbial contamination, and non-compliance with GMP standards. Next, we outline the essential components of a modern, compliant, and contamination-resistant Purified Water Storage and Distribution System.
Core Design Principles of Purified Water Storage and Distribution System
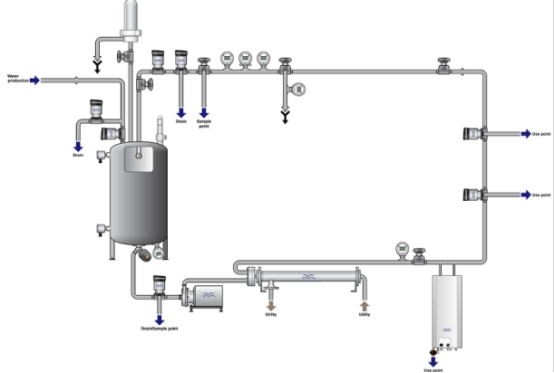
To ensure water quality at all times, modern pharmaceutical facilities use closed-loop PW systems that are designed to ensure the highest hygiene as well as continuous circulation and real-time monitoring. They are designed to provide purified water for injection (WFI) or purified water at every point of use, without compromising security or performance.
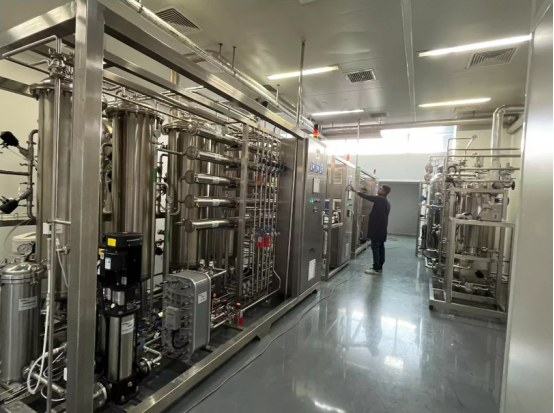

1) Thermal Loop Circulation
Continuous water circulation at higher temperatures is an established technique for controlling microbial growth for the PW system. This prevents the growth of biofilms and hinders the growth of microbial populations. The most effective method is to use thermal loops. method of keeping purified water for pharmaceutical use in a clean and constant condition.
In the case of ambient systems in which thermal disinfection is not possible, the combination of chemical or ozone sanitation, in conjunction with UV sterilization, will ensure that the levels of microbial contamination remain within the pharmacopeial limit.
Low-pressure boilers generally use soft water as make-up water; Medium-pressure boilers and some high-pressure boilers, demineralized water after dealkalization, desilication, desalting, and sodium ion exchange (medium-pressure boiler) is usually used as make-up water, while phosphate treatment is mainly used in the boiler.
For high-pressure and subcritical boilers, chemical demineralized water is generally used for make-up, while phosphate treatment or volatile treatment is used in the boiler. Volatility treatment must be adopted for a once-through boiler. In addition, the regulation of dissolved oxygen, salt content of boiler water, SiO2, and pH value in feedwater treatment is also more stringent due to the increase in boiler pressure.
2) Stainless Steel Piping and Hygienic Slope Design
Every one of the Purified Water Storage and Distribution Systems utilize stainless steel piping made of 316L that has electropolished internal surfaces. This ultra-smooth finish decreases the chance of adhesion between microbial and biofilm creation.
In addition, piping is installed with a slope of 3deg or more-to permit complete drainage and eliminate stagnant water. The sloped design is crucial in keeping contaminants out and also allows for periodic flushing of the system.
3) Zero Dead Leg and Continuous Flow Design
One of the key risk factors in the water treatment process in the pharmaceutical industry is the presence of dead legs, which are designed criteria typically restrict dead leg length—sections of pipework that do not allow water to flow. They can be sources of food for bacteria as well as endotoxins.
Modern PW distribution and storage systems are built with dead-leg valves with easily drainable samples ports with continuously flowing loops. The purified water keeps flowing, even past points of use to avoid stagnation and ensure the water’s quality throughout the entire system.
Contamination and Prevention Strategies
Preventing contamination is a top priority in the design and operation of any PW system. Microbial intrusion, endotoxin release, and particulate matter are the three major threats to purified water for pharmaceutical use.
The prevention of contamination is the top priority when designing and operating for the PW system. Microbial intrusion, endotoxin release and particulate matter are three most significant dangers to purified water for pharmaceutical use.

Microbial Control
- Hydrophobic 0.22 μm air filters at the vents of tanks stop airborne microbes and bacteria from entering the system.
- UV sterilizers on return lines clean water prior to re-entry into the tank for storage.
Insulation and temperature control also reduce the growth of microbial, particularly in thermally cleansed loops.
Endotoxin and Particle Control
Orbital weld can be used create smooth joints with no crevices that keep microbial contamination out and prevent particle accumulation.
Sloped pipes, in conjunction with regular draining and circulation flushing removes stagnant zones as well as reduces the risk of endotoxin.
The use of corrosion-resistant material reduces the amount of particulate that is shed and prolongs the life of the system.

Intelligent Monitoring and Alarm Systems
Digital transformation is changing the way PW systems. Automated and real-time analytics are crucial to the process of ensuring GMP performance and compliance.
Real-Time Quality Monitoring
Modern PW storage and distribution systems integrate advanced sensors to monitor:
- Conductivity – detects the presence of ionic contamination.
- TOC (Total Organic Carbon) is a measure of organic load.
- Microbial indicators allow an early identification of contaminants.
These parameters are tracked 24 hours a day every day, and any deviation sets off alarms, and correction actions..
PLC / SCADA Integration for Full Control
Integrating to PLC (Programmable Logical Controller) as well as SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems offers:
- Remote monitoring and configuration
2. Data logging and historical trend analysis
3. Electronic records that are audit-ready (ERES)
4. Control of access based on roles and Data integrity security
Why Choose Molewater for Purified Water Storage and Distribution System?
Molewater is a specialist in developing and manufacturing the most sophisticated PW distribution and storage systems to support pharmaceutical applications. Every PW system is designed to ensure that water quality is consistent as well as hygienic safety and complete regulatory compliance. Molewater’s systems are compatible with ambient and thermal distribution loops, and can be adapted to meet specific requirements of production.
Key Features of Molewater PW Systems:
- Fully customizable closed-loop architectures
- The use of pharmaceutical-grade stainless steel and tank materials
- integrated UV sterilization unit, with ozone injection and filters
- Intelligent monitoring systems that provide live alerts as well as audit logs.
Through minimizing interventions by hand and maximizing automation, Molewater aids pharmaceutical businesses keep their compliance on track while increasing the efficiency of their operations. If your facility requires the purification of drinking water or the purification of water used in pharmaceutical production.

In the strict regulatory context in the pharmaceutical industry, maintaining the integrity of distribution and storage systems is crucial. A properly designed PW system does not just protect against contamination, but also guarantees the compliance of customers, cuts down on the cost of maintenance, and aids in efficient operation. As the need for top-quality pure water for use in pharmaceuticals increases, the importance of a well-designed hygiene-conscious design in the process of water treatment in the pharmaceutical industry is becoming increasingly essential. Rely on Molewater to supply systems that are up to the most stringent standards of security, reliability, and regulatory compliance.





